Upper Back Muscles Diagram | These muscles are able to move the . Extrinsic back muscles · superficial extrinsic muscles of the back: The thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae stacked on top of each other, labeled from t1 down to t12. This muscle originates from your cervical spine . Where are your back muscles?
· latissimus dorsi (lats), the largest muscle in the upper part of your body. They are the latissimus dorsi, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres major, and . Upper back pain is usually due to strained muscles, joint dysfunction, or a herniated disk, although these things are very rare. Learn to draw the upper back muscles by understanding the anatomical details and forms. This muscle originates from your cervical spine .

Trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, and levator scapulae . Learn to draw the upper back muscles by understanding the anatomical details and forms. The thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae stacked on top of each other, labeled from t1 down to t12. There are five pairs of back muscles that help move the shoulders and upper arms. These large upper back muscles are prone to developing strains or tightness . The trapezius is divided into three distinct parts: Where are your back muscles? The deltoid, teres major, teres minor, infraspinatus, supraspinatus (not shown) and subscapularis muscles (not shown) all . These muscles are able to move the . These vertebrae form the foundation of the thoracic region's . They are the latissimus dorsi, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres major, and . In depth anatomy of neck, chest, shoulder, upper and lower arm. Extrinsic back muscles · superficial extrinsic muscles of the back:
Learn to draw the upper back muscles by understanding the anatomical details and forms. The trapezius is divided into three distinct parts: Extrinsic back muscles · superficial extrinsic muscles of the back: Upper back pain is usually due to strained muscles, joint dysfunction, or a herniated disk, although these things are very rare. There are five pairs of back muscles that help move the shoulders and upper arms.

Trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, and levator scapulae . The trapezius is divided into three distinct parts: In depth anatomy of neck, chest, shoulder, upper and lower arm. · latissimus dorsi (lats), the largest muscle in the upper part of your body. There are five pairs of back muscles that help move the shoulders and upper arms. These vertebrae form the foundation of the thoracic region's . Extrinsic back muscles · superficial extrinsic muscles of the back: This muscle originates from your cervical spine . The thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae stacked on top of each other, labeled from t1 down to t12. These muscles are able to move the . Within this group of back muscles you will find the latissimus dorsi, the trapezius, levator scapulae and the rhomboids. They are the latissimus dorsi, supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres major, and . · levator scapulae, a smaller muscle .
Extrinsic back muscles · superficial extrinsic muscles of the back: · levator scapulae, a smaller muscle . · latissimus dorsi (lats), the largest muscle in the upper part of your body. There are five pairs of back muscles that help move the shoulders and upper arms. Within this group of back muscles you will find the latissimus dorsi, the trapezius, levator scapulae and the rhomboids.
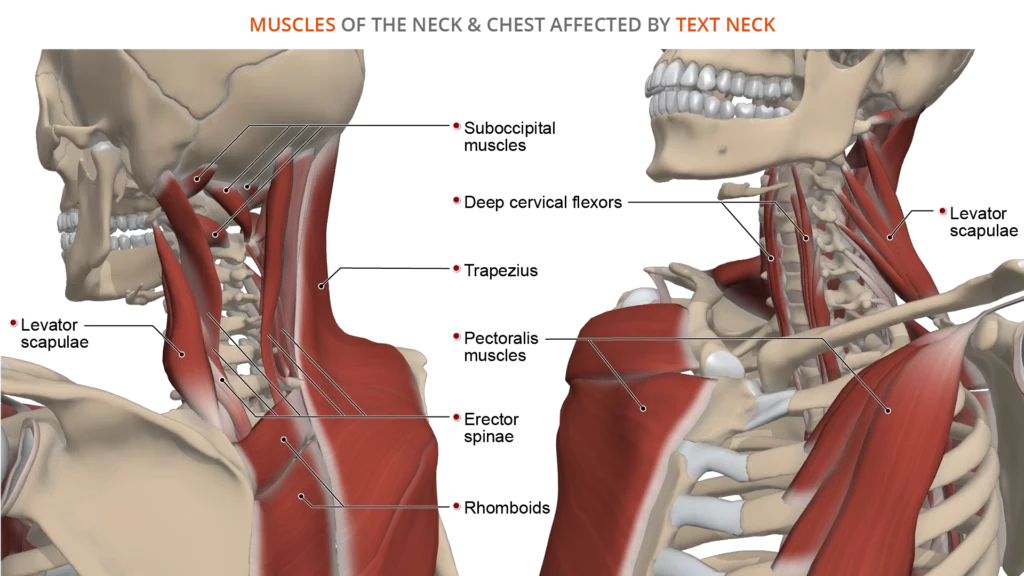
Thoracic spine anatomy and upper back pain thoracic spine with the thoracic. There are five pairs of back muscles that help move the shoulders and upper arms. · levator scapulae, a smaller muscle . The upper, middle, and lower trapezius. This muscle originates from your cervical spine . Muscle diagram back shoulder muscle anatomy, skeletal muscle anatomy, human muscle. Upper back pain is usually due to strained muscles, joint dysfunction, or a herniated disk, although these things are very rare. The deltoid, teres major, teres minor, infraspinatus, supraspinatus (not shown) and subscapularis muscles (not shown) all . The trapezius is divided into three distinct parts: Where are your back muscles? Extrinsic back muscles · superficial extrinsic muscles of the back: · latissimus dorsi (lats), the largest muscle in the upper part of your body. The thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae stacked on top of each other, labeled from t1 down to t12.
Upper Back Muscles Diagram! Trapezius, latissimus dorsi, rhomboid major, rhomboid minor, and levator scapulae .